Private 5G: A global overview
Private 5G refers to a 5G mobile system built and operated exclusively for the private use of a company, user, or government agency. A private 5G network is defined in 3GPP as a non-public network NPN. It typically uses a smaller, more focused implementation to meet the specific reliability, availability, and service needs of an organization.
Private 5G networks are the catalyst for the fourth industrial revolution. The list of deployment options is growing and the expected benefits are many.
By offering ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC), private 5G networks change the equation. It takes part in the advanced Internet of Things (IoT), the fourth industrial revolution, and critical public safety applications. Improved access to full-spectrum, business case specialization, and network security issues
are other strategic factors of the private 5G market.
Being able to connect a large number of devices in a moving environment, the private 5G network outpaces Ethernet by not using expensive and bulky wired equipment. In the radio domain, private 5G networks offer spectrum flexibility, high data rates (several Gbps), ultra-low latency, increased and reliable connectivity.
To build truly isolated networks, vertical network slicing, private Edge Computing, and improved security are a must. These radio and network advantages make private 5G better than private LTE networks.
Benefits of private 5G
It should be noted that, through its simplifying virtues, a private 5G network solves many problems, including interference management.
Constant availability : The availability of communication services is defined by:

In private 5G networks, it ranges from critical values (e.g. 99.999999%) to modest values (e.g. 99.9%), depending on the use case.
Increased reliability: Reliability refers to the ability of the communication service to function as expected during a given time interval under given conditions. In particular, wireless IoT and IIoT systems require industry-leading reliability to complete complex tasks.
Ultra-low latency: ultra-low latency refers to a network’s ability to facilitate mission-critical applications that require end-to-end latency of less than one millisecond. This characteristic is particularly important for industrial automation.
It makes human-machine interactions more reliable. Each step of the uplink/downlink 5G transmission process has been rethought to minimize latency. To that end, 5G New Radio (NR) uses new numbering, fewer allowed retransmissions, and advanced scheduling algorithms.
High device density with high throughput: Many applications in 5G private networks require the use of heterogeneous devices: fixed, ad hoc, and mobile (sensors, actuators, programmable logic controllers, mobile robots, cameras, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) related devices, etc.) Connectivity supporting high data rates is deployed to perform high-speed, high-precision machine tasks.
High security: 5G private networks feature enhanced security through the use of network isolation and device/user authentication. Therefore, enterprises or operating entities gain sovereignty by keeping sensitive data local. Transmissions are highly secure over public networks, which is essential for critical applications (military, industrial, etc.).
Stable and customizable quality of service: Performance indicators (throughput, latency, packet loss rate, etc.) are better controlled in private 5G networks. In addition, system performance, as well as resource utilization, adapts to network specifications based on local statistics. It is also possible to establish B2B communications via public and non-public 5G networks. For example, continuity of service is required when a vehicle moves from a factory (served by a private 5G network) to the outside (served by a public 5G network)
Private 5G: The Future Outlook (2022-2030)
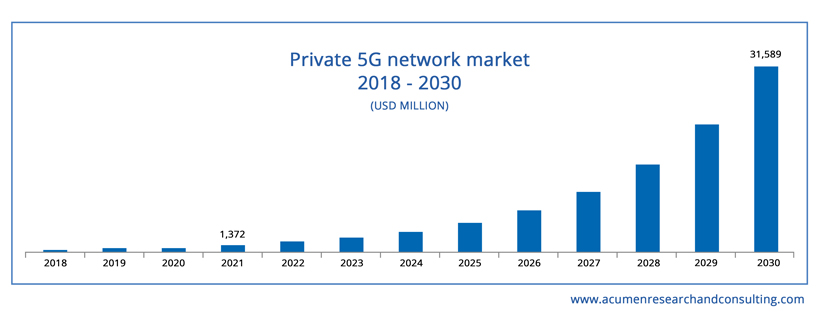
According to Globe Newswire, the global private 5G network market size is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 42.4% and reach a market value of approximately USD 31,589 million by 2030. The concept of private 5G networks is familiar, but the emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT) and connected assets will catalyze its impacts on organizations.
The global private 5G network market size is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 42.4% by 2030. – Globe Newswire
Companies will now have the option to build and operate their own private 5G network or outsource it to a systems integrator or mobile network operator. This triggers new opportunities for all types of organizations: retail, medical, entertainment, manufacturing, transportation, and education.
700 enterprise technology decision-makers speculated about 5G, with the majority saying it will bring new opportunities for their business (80%), function (79%), and industry (79%). – Verizon
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the global 5G private network market
Due to the disruption of future trials and testing required to certify the stability and performance of 5G autonomous networks, the COVID-19 pandemic is expected to delay the introduction of widespread private 5G infrastructure.
7 out of 10 decision-makers believe 5G will help their companies deal with the impact of COVID-19. – Verizon
Remote sensing, improved video quality, reduced latency, and high bandwidth are all benefits of private 5G that can be used to enhance the telecommuting experience across all verticals. The market experienced a significant slowdown in 2020 but will return to normal growth in the coming years.
Growth aspects of the global private 5G network market
The number of internet users is increasing rapidly due to increased investments, advances in technology infrastructure, and decreasing data plans. Many industries are adopting Industry 4.0 on a large scale to improve productivity and efficiency.
In this sense, several key industry operators such as ABB Ltd, Mercedes-Benz AG, and Siemens AG have started deploying sensor-based technologies and industrial robotics.
The 5G private network is a major part of this momentum. It offers strategic advantages such as wireless security, lower latency, network slicing, improved bandwidth, and ultra-reliable connectivity.
The market is, however, held back by high initial investment costs and the effects of COVID-19 pandemic. On the other hand, the steadily growing demand from private networks and the substantial government funding for 5G infrastructures are expected to create many opportunities for the market in the coming period.
Market Segmentation
The global 5G private networks market has been segmented based on component, frequency, spectrum, and vertical.
Based on the component: the market is divided into hardware (core network, radio access network, backhaul, and transport), software, and service (data services, installation and integration, support, and maintenance). The hardware segment leads the component market, while the software segment is expected to grow at a significant rate by 2030.
Based on frequency: The frequency segment is divided into Sub-6 GHz and mmWave. There are licensed and unlicensed/shared frequencies. The unlicensed/shared segment occupied a considerable market share in 2021.
Countries such as Russia, Japan, South Korea and Italy have launched mmWave frequencies to enhance data services. Thus, the focus of major federal governments on providing mmWave frequencies is expected to increase the growth of the mmWave segment by 2030.
Based on a spectrum: The spectrum segment consists of licensed and unlicensed/shared spectrum. Unlicensed spectrum bandwidth is readily available and highly preferred for massive machine-type communications (mMTC). Licensed spectrum is more costly than unlicensed/shared spectrum.
That is dueto the fact that an organization must purchase a full license for a particular bandwidth to enhance and secure connectivity. Access to licensed spectrum can also be obtained from communication service providers.
Many countries such as the United States and Germany use licensed spectrum for their applications. Thus, the increasing demand for highly secure connectivity for mission-critical applications is expected to drive the growth of the licensed spectrum segment by 2030.
Based on vertical: The vertical segment is categorized into manufacturing/plant (automotive, apparel & accessories, food & beverage, electrical & electronics, heavy machinery, pharmaceuticals, etc.), enterprise & campus, mining, defense, retail, healthcare/hospitals, agriculture, transportation & logistics, oil & gas, energy & utilities, smart cities, etc.
The manufacturing/plant segment generated the largest revenue share due to the focus on increasing the adoption of private 5G networks. The increasing need for uninterrupted communication between machines is expected to drive growth in all vertical segments by 2030.
Regional Overview
The regional classification of the global private 5G networks market consists of North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa. In 2021, North America captured the majority of the regional market share.
This can be attributed to the adoption of 5G, AI, IoT, and the existence of many technologically advanced companies. However, the Asia Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth rate by 2030.
Some of the factors driving the private 5G network market in the Asia Pacific are increasing investment in 5G infrastructure, increased automation in many industries, and the high growth potential of several smart cities.
Major players
Major players covered globally include :
- Ericsson
- Huawei Technologie
- Nokia Corp
- Samsung
- Athonet
- Druid Software
- Airspan
This article is a summary of the report published by Acumen Research and Consulting entitled “5G Private Networks Market – Global Industry Analysis, Market Size, Opportunities and Forecast, 2022-2030”. We began by presenting the definition and benefits of 5G private and then provided an overview of how it is expected to evolve by 2030.
Conclusion
Different solutions are emerging today between license or not, slicing and public network, it is the specific use cases that will determine the best type of connectivity.
In addition, the emergence of certain countries ahead of private networks by the allocation of frequencies such as the USA, Germany and the United Kingdom highlights that manufacturers are not the only decision-makers of their future in industry 4.0, but a strong link exists with each national regulator who wants to allocate frequencies or not for private networks.
As such and in order not to leave aside many European companies in this race, Privinnet co-created EUWENA in order to highlight at European level the needs of manufacturers and the entreprises end-users in private 5G networks.
It is absolutely necessary to be able to have as in the USA, in Germany in the UK, now in France but also in all the countries of Europe of frequencies if possible harmonized in order to benefit from the best possible eco-system.
Tomorrow’s competitiveness will go through this harmonization and EUWENA was created to defend these interests with national regulators little known to the verticals and the European community.
Privinnet will also be there to highlight the use cases most sensitive to this so-called critical connectivity and can also promote the adoption of these new technologies through personalised support (interviews, 1-hour mini-trainings, sharing of experience, etc.)


